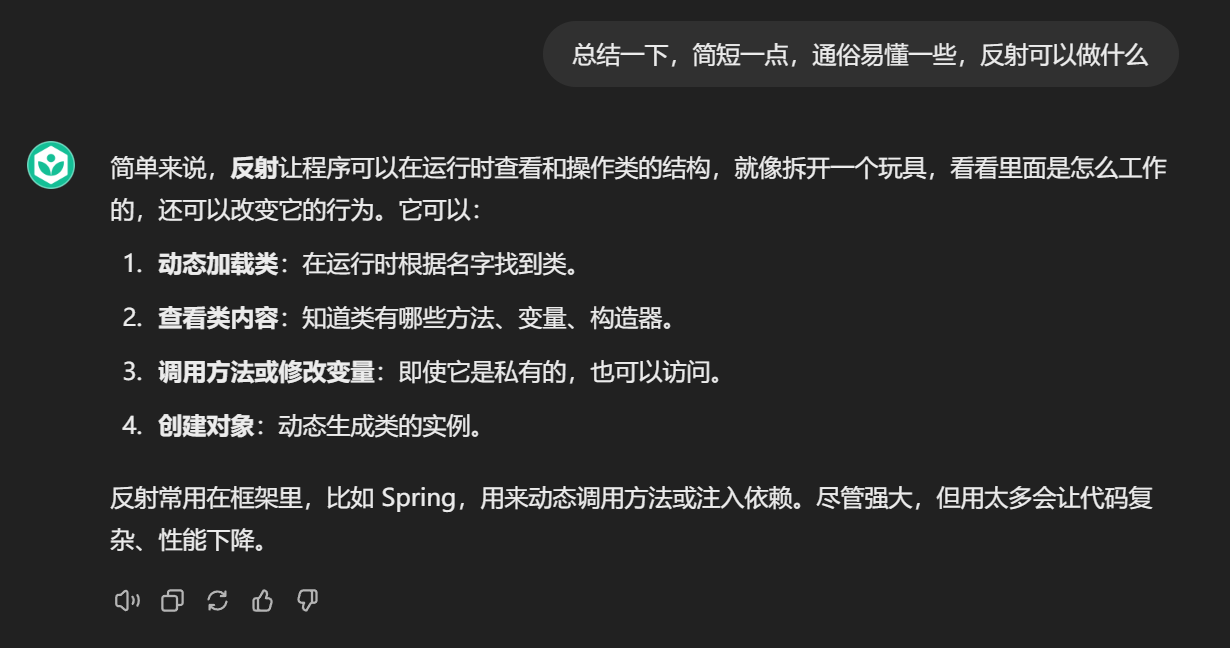
什么是反射呢?
来看看GPTs的回答!
三种获取class的方式
- 01
- 02
- 03
- 04
- 05
- 06
- 07
- 08
- 09
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
// 获取class
Class<? extends User> aClass = User.class;
try {
// 第一种方式,通过class创建对象
User user1 = (User) aClass.getConstructor().newInstance();
System.out.println(user1);
// 第二种方式,通过forName加载类,然后反射创建对象
Class<?> bclass = Class.forName("com.example.advancedlearning.entity.User");
User user2 = (User) bclass.getConstructor().newInstance();
System.out.println(user2);
//new User
User newUser = new User();
// 获取classs
Class<? extends User> cclass = newUser.getClass();
// class肯定都是相等的
System.out.println(aClass == bclass);
System.out.println(aClass == cclass);
// 对象肯定都是不相等的
System.out.println(user1 == user2);
System.out.println(user1 == newUser);
} catch (InstantiationException | IllegalAccessException | ClassNotFoundException | InvocationTargetException |
NoSuchMethodException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}反射如何创建有参构造函数对象?
- 01
- 02
- 03
- 04
- 05
- 06
- 07
- 08
- 09
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
try {
Class<?> aClass = Class.forName("com.example.advancedlearning.entity.User");
// 通过class创建的对象,默认走的是无参构造函数
// getConstructor只能拿到public的构造函数
User user1 = (User) aClass.getConstructor().newInstance();
System.out.println(user1);
System.out.println("----------------------------------");
// 通过getDeclaredConstructor可以拿到所有的构造函数,但是需要setAccessible(true)来访问private的构造函数
User user2 = (User) aClass.getDeclaredConstructor(String.class, Integer.class).newInstance("zhangsan", 20);
System.out.println(user2);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException | InstantiationException | IllegalAccessException | NoSuchMethodException |
InvocationTargetException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
反射里的API
通过反射拿到类的字段
- 01
- 02
- 03
- 04
- 05
- 06
- 07
- 08
Class<?> aClass = Class.forName("com.example.advancedlearning.entity.User");
// 通过getDeclaredFields可以拿到所有的字段
// getFields只能拿到public的字段
Field[] declaredFields = aClass.getDeclaredFields();
for (java.lang.reflect.Field field :declaredFields) {
System.out.println("字段名:" + field.getName());
System.out.println("字段类型:" + field.getType());
}给public和private属性赋值
- 01
- 02
- 03
- 04
- 05
- 06
- 07
- 08
- 09
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
try {
Class<?> aClass = Class.forName("com.example.advancedlearning.entity.User");
// 通过getDeclaredFields可以拿到所有的字段
// getFields只能拿到public的字段
Field[] declaredFields = aClass.getDeclaredFields();
for (java.lang.reflect.Field field :declaredFields) {
System.out.println("字段名:" + field.getName() + ", 字段类型:" + field.getType());
}
// 给publicUser公共字段赋值
User user = (User) aClass.getConstructor().newInstance();
Field publicUser = aClass.getField("publicUser");
// publicUser.setAccessible(true);
publicUser.set(user, "lisi");
// 给private属性userName赋值
Field userName = aClass.getDeclaredField("userName");
userName.setAccessible(true);// setAccessible是为了访问private属性
userName.set(user, "wangwu");
System.out.println(user);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException | NoSuchMethodException | NoSuchFieldException | InstantiationException |
IllegalAccessException | InvocationTargetException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}拿到所有方法,调用私有方法和调用私有带参数方法
- 01
- 02
- 03
- 04
- 05
- 06
- 07
- 08
- 09
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
try {
Class<?> aClass = Class.forName("com.example.advancedlearning.entity.User");
// 在JDK17中,通过反射创建对象,需要用getConstructor方法
// 而不是newInstance(),因为newInstance()方法已经被废弃
// 为了确保兼容性和安全性,使用getConstructor().newInstance()来创建对象
User user = (User) aClass.getConstructor().newInstance();
// 拿到所有的方法
java.lang.reflect.Method[] methods = aClass.getMethods();
for (java.lang.reflect.Method method : methods) {
System.out.println("方法名:" + method.getName()
+ ", 返回类型:" + method.getReturnType()
+ ", 参数类型:" + Arrays.toString(method.getParameterTypes()));
}
// 分割线
System.out.println("----------------------------------");
// 调用mayikt方法
Method mayikt = aClass.getDeclaredMethod("mayikt");
mayikt.setAccessible(true); // setAccessible是为了访问private属性
Object invoke = mayikt.invoke(user);// invoke是为了调用private方法
// 调用私有方法sum方法传入两个参数
Method sum = aClass.getDeclaredMethod("sum", Integer.class, Integer.class);
sum.setAccessible(true);
Integer integer = (Integer) sum.invoke(user, 10, 20);
System.out.println("调用sum方法返回值:" + integer);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException | NoSuchMethodException | InstantiationException | IllegalAccessException |
InvocationTargetException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}通过反射越过泛型检查
- 01
- 02
- 03
- 04
- 05
- 06
- 07
- 08
- 09
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
try {
// 创建一个字符串集合
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add("zhangsan");
// 通过反射机制调用add方法,传一个int类型的参数
Class<?> aClass = list.getClass();
Method add = aClass.getDeclaredMethod("add", Object.class);
add.setAccessible(true);
add.invoke(list, 10);
// 泛型检查只有在编译时存在,可以通过反射直接越过泛型检查
System.out.println(list);
// 虽然是越过了泛型检查,但是lombok会报错
list.forEach(System.out::println);
} catch (NoSuchMethodException | IllegalAccessException |
InvocationTargetException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
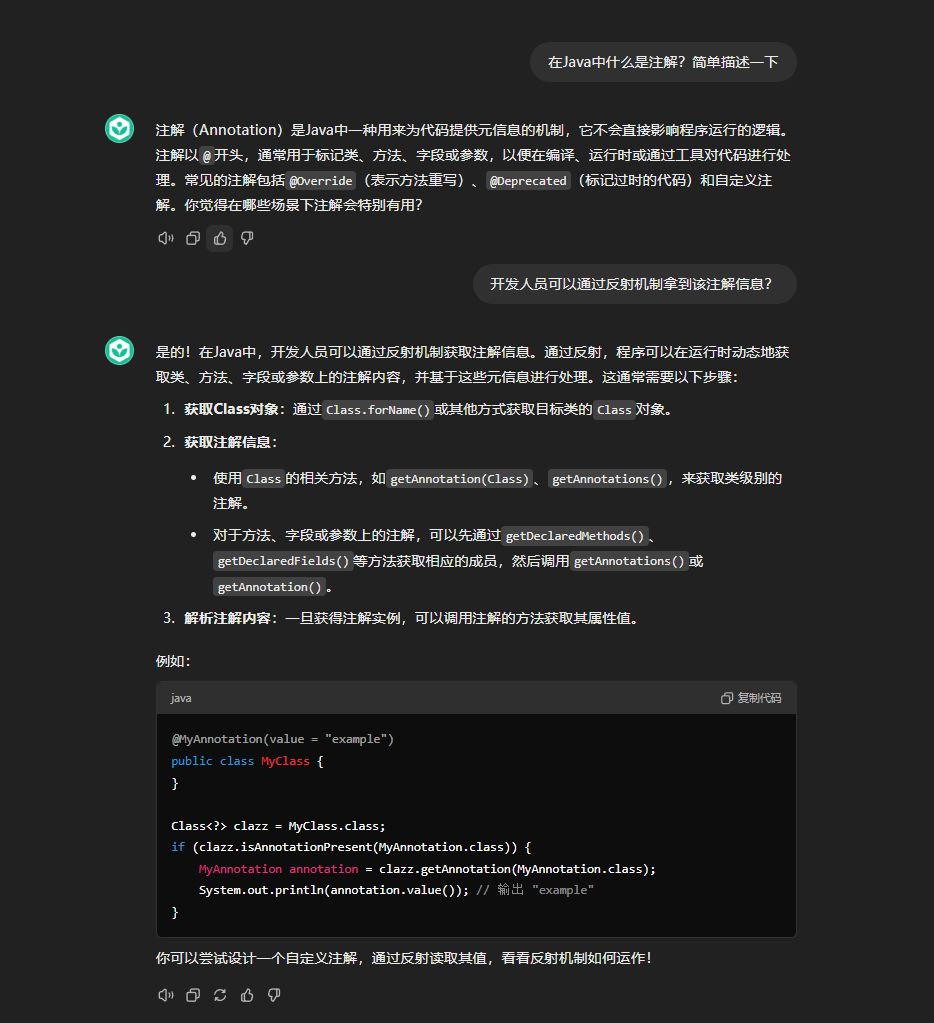
}什么是注解?
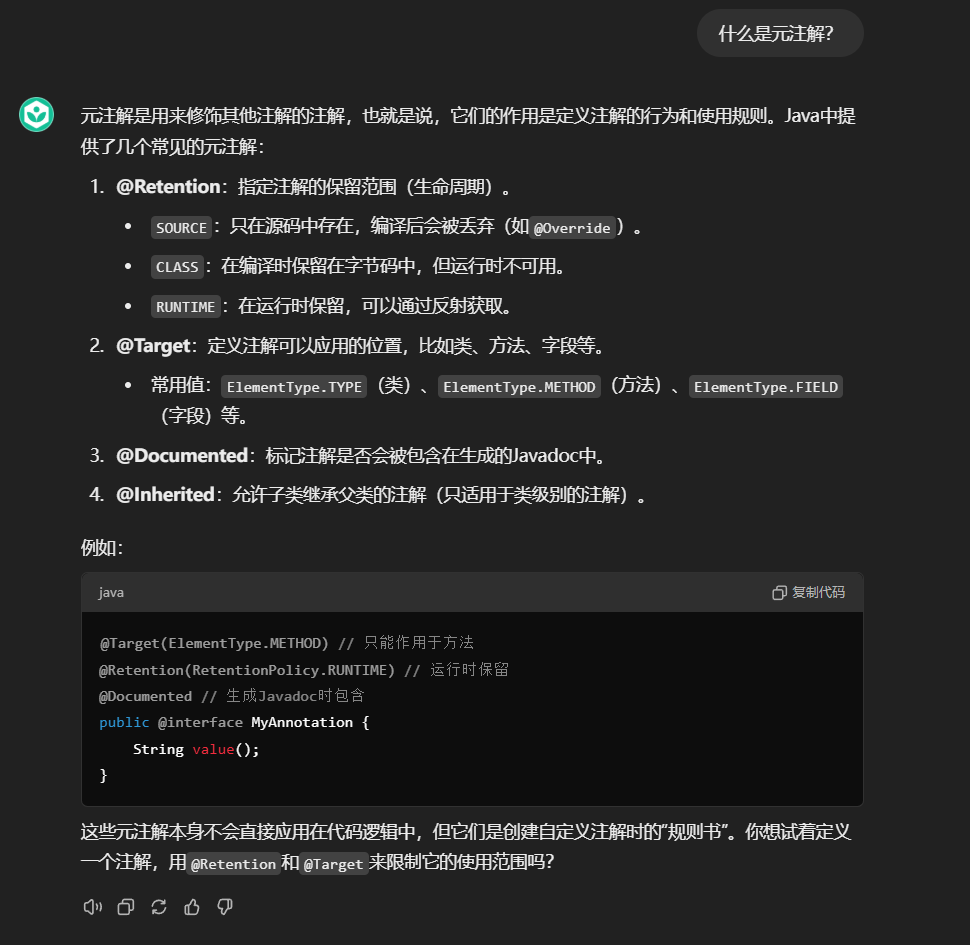
什么是元注解?
获取方法上的注解
- 01
- 02
- 03
- 04
- 05
- 06
- 07
- 08
- 09
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
try {
Class<?> aClass = Class.forName("com.example.advancedlearning.entity.User");
// 创建对象
User user = (User) aClass.getConstructor().newInstance();
// 获取mayikt方法
Method mayikt = aClass.getDeclaredMethod("mayikt");
// 获取mayikt方法的注解
MyAnnotation myAnnotation = mayikt.getDeclaredAnnotation(MyAnnotation.class);
System.out.println(myAnnotation.annotationType().getName());
} catch (ClassNotFoundException | NoSuchMethodException | InstantiationException | IllegalAccessException |
InvocationTargetException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}获取类上的注解
- 01
- 02
- 03
- 04
- 05
- 06
try {
Class<?> aClass = Class.forName("com.example.advancedlearning.entity.User");
MyAnnotation myAnnotation = aClass.getDeclaredAnnotation(MyAnnotation.class);
System.out.println(myAnnotation);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}获取字段上的注解
- 01
- 02
- 03
- 04
- 05
- 06
- 07
try {
Class<?> aClass = Class.forName("com.example.advancedlearning.entity.User");
java.lang.reflect.Field userName = aClass.getDeclaredField("userName");
MyAnnotation myAnnotation = userName.getDeclaredAnnotation(MyAnnotation.class);
System.out.println(myAnnotation);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException | NoSuchFieldException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}获取构造函数上的注解
- 01
- 02
- 03
- 04
- 05
- 06
- 07
- 08
- 09
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
try {
Class<?> aClass = Class.forName("com.example.advancedlearning.entity.User");
// 获取构造函数对象
Constructor<?> constructor = aClass.getDeclaredConstructor(String.class, Integer.class);
MyAnnotation myAnnotation = constructor.getDeclaredAnnotation(MyAnnotation.class);
System.out.println(myAnnotation);
// 获取无参构造函数
Constructor<?> constructor1 = aClass.getDeclaredConstructor();
MyAnnotation myAnnotation1 = constructor1.getDeclaredAnnotation(MyAnnotation.class);
System.out.println(myAnnotation1);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException | NoSuchMethodException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}反射+注解实现功能
MyCurrentLimit
- 01
- 02
- 03
- 04
- 05
- 06
- 07
- 08
- 09
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
// 限流注解
public MyCurrentLimit {
/**
* name 限流名称
*/
String name() default "";
/**
* limit 每秒限制多少次
*/
int limit() default 10;
}
CurrentLimitAop
- 01
- 02
- 03
- 04
- 05
- 06
- 07
- 08
- 09
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
import com.example.advancedlearning.annotation.MyCurrentLimit;
import com.example.advancedlearning.common.Result;
import com.google.common.util.concurrent.RateLimiter;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.Signature;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Around;
import org.aspectj.lang.reflect.MethodSignature;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap;
public class CurrentLimitAop {
// 整一个ConcurrentHashMap来存储每个接口的RateLimiter
private ConcurrentHashMap<String, RateLimiter> rateLimiterMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
/**
* Spring AOP 相关注解
* 在使用 @Aspect 的切面类中,通常会结合其他注解来定义切入点和通知:
*
* @Pointcut: 定义切入点,指定在哪些方法上执行增强逻辑。
* @Before: 定义前置通知,在目标方法执行前执行。
* @After: 定义后置通知,在目标方法执行后执行。
* @AfterReturning: 定义返回通知,在目标方法正常返回后执行。
* @AfterThrowing: 定义异常通知,在目标方法抛出异常时执行。
* @Around: 定义环绕通知,可以控制目标方法的执行时机、参数和返回值。
*/
// 环绕通知com.example.advancedlearning.annotation.MyCurrentLimit
public Object around(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp) {
/*
环绕通知更好的控制方法是否执行!
*/
try {
// 获取signature,signature是一个方法签名对象
Signature signature = pjp.getSignature();
// 强转成方法签名对象
MethodSignature methodSignature = (MethodSignature) signature;
// 拿到注解的limit值
MyCurrentLimit myCurrentLimit = methodSignature.getMethod().getAnnotation(MyCurrentLimit.class);
// 拿到注解的name值
String name = myCurrentLimit.name();
// 拿到注解的limit值
int limit = myCurrentLimit.limit();
// 从rateLimiterMap中获取RateLimiter对象,如果没有则创建一个
RateLimiter rateLimiter = rateLimiterMap
.computeIfAbsent(name, k -> RateLimiter.create(limit));
if (!rateLimiter.tryAcquire()) {
return Result.error("访问太频繁啦!");
}
// 限流
System.out.println("name: " + name + ", limit: " + limit);
// 放行目标方法
return pjp.proceed();
} catch (Throwable e) {
log.error("未知异常:{}", e.getMessage(), e);
return Result.error("哎呀,服务器繁忙啦!");
}
}
}
MemberController
- 01
- 02
- 03
- 04
- 05
- 06
- 07
- 08
- 09
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
import com.example.advancedlearning.annotation.MyAnnotation;
import com.example.advancedlearning.annotation.MyCurrentLimit;
import com.example.advancedlearning.common.Result;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class MemberController {
public Result<String> get() {
return Result.success("hello");
}
public Result<Map<String, Object>> test() {
Map<String, Object> data = new HashMap<>();
data.put("name", "张三");
data.put("age", 18);
return Result.success("获取成功", data);
}
public Result<String> add() {
return Result.success("This is a Addd Method");
}
public Result<String> delete() {
return Result.success("This is a Delete Method");
}
public Result<String> update() {
return Result.success("This is a Update Method");
}
}